Loading
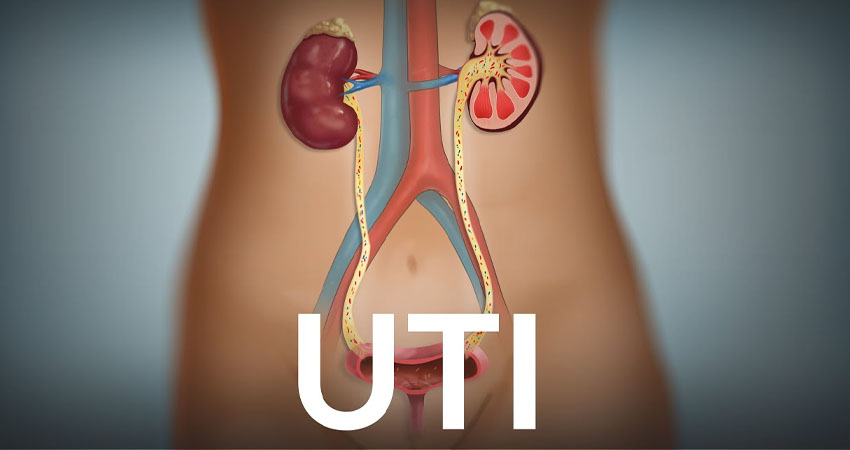
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) occur when bacteria enter the urinary system, typically affecting the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis), or kidneys (pyelonephritis). They are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.